 CENTRAL
PROCESSING UNIT
CENTRAL
PROCESSING UNIT
|
|
 |
1]
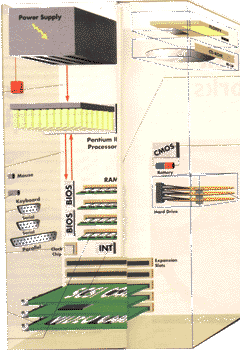
When you turn on your PC, a process called the POST (power on self test)
begins with an electrical signal following a permanently programmed path
to the CPU, or microprocesso. There, the electrical signal clears leftover
data from the chip's internal memory registers. The signal alsoi resets
a CPU register called the program counter to a specific number. In the
case of ATs and later computers, the hexa decimal number is F000. The
number in the program counter tells the CPU the address of the next instruction
that needs processing . In this case, the address is the beginning of
a boot program stored permanently at the address F000 in a set of read-only
memory(ROM) chips that contain the PC's basic input/output system (BIOS).
|
|
3]
The CPU sends signals over the system bus-the circuits that connect all
the components with each other-to make sure that they are al functioning.
4] The CPU also checks the system's timer, or clock, which is reponsible for pacing signals to make sure all the PC's operations function in a synchronized, orderly fashion. 5] The POST tests the memory contained on the display adapter and the video signals that control the display. It then makes the adapter's BIOS code a part of the system's overall BIOS and memory configuration. It's at this point that you'll first see something appear on your PC's monitor. 6] The POST runs a series of tests to ensure that the RAM chips are functioning properly. The tests write data to each chip, then read it and compare what they read with the data sent to the chips in the first place. On some PCs at this point, you'll see on the monitor a running account of the amount of memory that's been checked. 7] The CPU vertifies that the keyboard is attched properly and determines whether any keys have been pressed. 8] The POST sends signals over specific paths on the bus to the floppy and hard disk drives and listens for a response to determine which drives are available. 9] The results of the POST tests are compared with data in a specific CMOS chip that is the official record of which components are installed. CMOS is a typed of memory chip that retains its data when power is turned off, as long as it receives a trickle of electricity from a battery. Any changes to the basic system configuration must be recorded in the CMOS setup. If the tests detect new hardware, you're given a chance to update the configuration on the setup screen. 10] Some system's components, such as SCSI controller card , contain a BIOS which interprets commands from the processor to control that hardware. Those components BIOS codes are incorporated as part of the system's own overall BIOS. Sometimes these BIOS codes are copied from the slow CMOS BIOS chip to the PC's faster RAM.Newer PCs may also run a Plug and Play opeartion to distribute system resource among different components. The PC is now ready to take the next step in the boot process: loading an operating system from disk. |